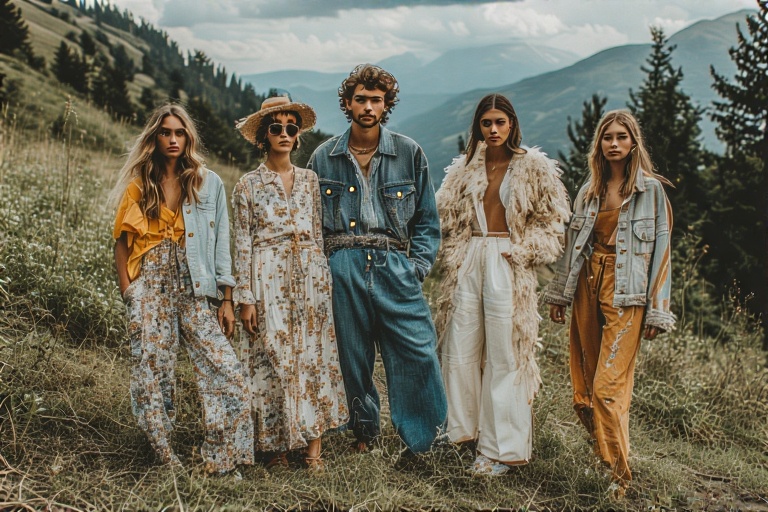
The Rise of Slow Fashion
What is Slow Fashion?
The Rise of Slow Fashion represents a deliberate counterpoint to the fast fashion model, which churns out cheap, trend-driven clothing at breakneck speed. Slow fashion emphasizes quality, ethical production, and sustainability. It encourages consumers to invest in well-made, durable garments that stand the test of time, both in style and construction. Unlike fast fashion’s focus on quantity, The Rise of Slow Fashion champions mindfulness—urging people to buy less, choose better, and value the story behind their clothes.
The term “slow fashion” was coined in 2007 by Kate Fletcher, a design activist and professor, who drew inspiration from the slow food movement. Just as slow food prioritizes local, sustainable ingredients, The Rise of Slow Fashion advocates for transparency, fair labor practices, and eco-friendly materials. It’s about fostering a deeper connection between consumers, producers, and the planet.
Why The Rise of Slow Fashion Matters
The environmental toll of fast fashion is staggering. According to the United Nations, the fashion industry accounts for 10% of global carbon emissions and 20% of wastewater. Fast fashion’s reliance on synthetic fibers, like polyester, contributes to microplastic pollution, while its rapid production cycles generate millions of tons of textile waste annually. The Rise of Slow Fashion addresses these issues by promoting sustainable practices that reduce waste and pollution.
Beyond the environment, The Rise of Slow Fashion tackles social injustices. Fast fashion often relies on exploitative labor practices, with workers in developing countries earning meager wages in unsafe conditions. Slow fashion brands, on the other hand, prioritize fair wages, safe workplaces, and ethical supply chains. By supporting The Rise of Slow Fashion, consumers can align their values with their purchases, fostering a more equitable industry.
Core Principles of Slow Fashion
The Rise of Slow Fashion is guided by several key principles that set it apart from its fast-paced counterpart:
- Quality Over Quantity: Slow fashion encourages investing in fewer, high-quality pieces that last longer. A well-crafted jacket or a timeless dress can replace dozens of disposable items.
- Sustainability: From organic cotton to recycled materials, The Rise of Slow Fashion prioritizes eco-friendly fabrics that minimize environmental harm.
- Transparency: Slow fashion brands are open about their supply chains, ensuring consumers know where and how their clothes are made.
- Ethical Production: Fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for artisans are central to The Rise of Slow Fashion.
- Timeless Design: Unlike fast fashion’s fleeting trends, slow fashion focuses on classic, versatile pieces that remain stylish for years.
These principles empower consumers to make informed choices, contributing to The Rise of Slow Fashion as a movement for change.
The Consumer’s Role in The Rise of Slow Fashion
Consumers are at the heart of The Rise of Slow Fashion. By shifting their shopping habits, individuals can drive demand for sustainable and ethical clothing. Here are practical ways to embrace The Rise of Slow Fashion:
- Shop Secondhand: Thrift stores, vintage shops, and online platforms like Depop or Poshmark offer unique, pre-loved garments that reduce waste.
- Support Ethical Brands: Research brands that align with slow fashion values, such as Everlane, Reformation, or Patagonia, which prioritize sustainability and transparency.
- Care for Your Clothes: Proper maintenance, like washing in cold water or air-drying, extends the life of garments, supporting The Rise of Slow Fashion.
- Embrace Minimalism: Curate a capsule wardrobe with versatile, high-quality pieces that mix and match effortlessly.
- Learn to Repair: Mending small tears or replacing buttons can keep clothes in use longer, aligning with The Rise of Slow Fashion.
By making mindful choices, consumers fuel The Rise of Slow Fashion, encouraging brands to adopt sustainable practices.
The Role of Brands in The Rise of Slow Fashion
Brands play a pivotal role in The Rise of Slow Fashion. Many are rethinking their business models to prioritize sustainability and ethics. For example, Stella McCartney, a pioneer in slow fashion, uses vegan leather and organic materials while advocating for animal welfare. Similarly, smaller brands like People Tree and Thought Clothing focus on fair trade and eco-friendly production.
The Rise of Slow Fashion has also inspired innovation. Brands are experimenting with biodegradable fabrics, zero-waste designs, and circular fashion models, where garments are designed to be recycled or repurposed. By investing in sustainable practices, these brands prove that style and responsibility can coexist, furthering The Rise of Slow Fashion.
Challenges Facing The Rise of Slow Fashion
Despite its growth, The Rise of Slow Fashion faces obstacles. One major challenge is accessibility. High-quality, ethical clothing often comes with a higher price tag, making it less affordable for some consumers. However, The Rise of Slow Fashion counters this by emphasizing long-term value—spending more upfront on durable pieces saves money over time compared to frequently replacing cheap items.
Another challenge is greenwashing, where brands falsely claim to be sustainable. The Rise of Slow Fashion demands transparency, and consumers must research certifications like Fair Trade, GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard), or B Corp to verify claims. Education is key to overcoming these hurdles and sustaining The Rise of Slow Fashion.
The Economic and Cultural Impact of The Rise of Slow Fashion
The Rise of Slow Fashion is reshaping economies and cultures. By supporting local artisans and small businesses, it fosters economic resilience in communities often exploited by fast fashion. For instance, brands that work with traditional weavers or dyers preserve cultural heritage while providing fair livelihoods.
Culturally, The Rise of Slow Fashion encourages individuality. Instead of chasing trends, consumers are embracing unique, timeless styles that reflect their personalities. This shift is evident on platforms like Instagram and Pinterest, where slow fashion influencers showcase creative ways to style secondhand or sustainable pieces, amplifying The Rise of Slow Fashion.
The Future of The Rise of Slow Fashion
The trajectory of The Rise of Slow Fashion is promising. As climate change and social justice issues gain prominence, more consumers are demanding accountability from brands. Technology is also playing a role, with innovations like blockchain ensuring supply chain transparency and AI optimizing sustainable production processes.
Governments are stepping in too. In 2024, the European Union introduced regulations to curb textile waste and promote circular fashion, aligning with The Rise of Slow Fashion. As these trends continue, The Rise of Slow Fashion is poised to become the dominant model, transforming the industry for good.
Conclusion
The Rise of Slow Fashion is more than a trend—it’s a movement toward a more sustainable, ethical, and mindful way of consuming clothing. By prioritizing quality, transparency, and environmental stewardship, The Rise of Slow Fashion empowers consumers and brands to create a positive impact. While challenges like affordability and greenwashing persist, the growing demand for slow fashion signals a brighter future for the industry and the planet.
Embracing The Rise of Slow Fashion means choosing clothes that tell a story—of craftsmanship, care, and consciousness. It’s an invitation to rethink our relationship with fashion, making choices that align with our values and contribute to a better world.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between slow fashion and fast fashion?
Slow fashion focuses on quality, sustainability, and ethical production, while fast fashion prioritizes cheap, trend-driven clothing produced rapidly, often at the expense of the environment and workers.
2. How can I start embracing The Rise of Slow Fashion?
Begin by shopping secondhand, supporting ethical brands, maintaining your clothes properly, and building a capsule wardrobe with timeless pieces.
3. Is slow fashion more expensive?
Slow fashion items may have a higher upfront cost, but their durability and timeless design make them cost-effective over time, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
4. How can I spot greenwashing in fashion brands?
Look for certifications like Fair Trade or GOTS, research the brand’s supply chain, and be wary of vague claims like “eco-friendly” without evidence.
5. Why is The Rise of Slow Fashion important for the environment?
Slow fashion reduces waste, lowers carbon emissions, and minimizes pollution by using sustainable materials and ethical production methods, unlike fast fashion’s harmful practices.
6. Can slow fashion be stylish?
Absolutely! The Rise of Slow Fashion emphasizes timeless, versatile designs that allow for creativity and individuality, making it easy to stay stylish sustainably.